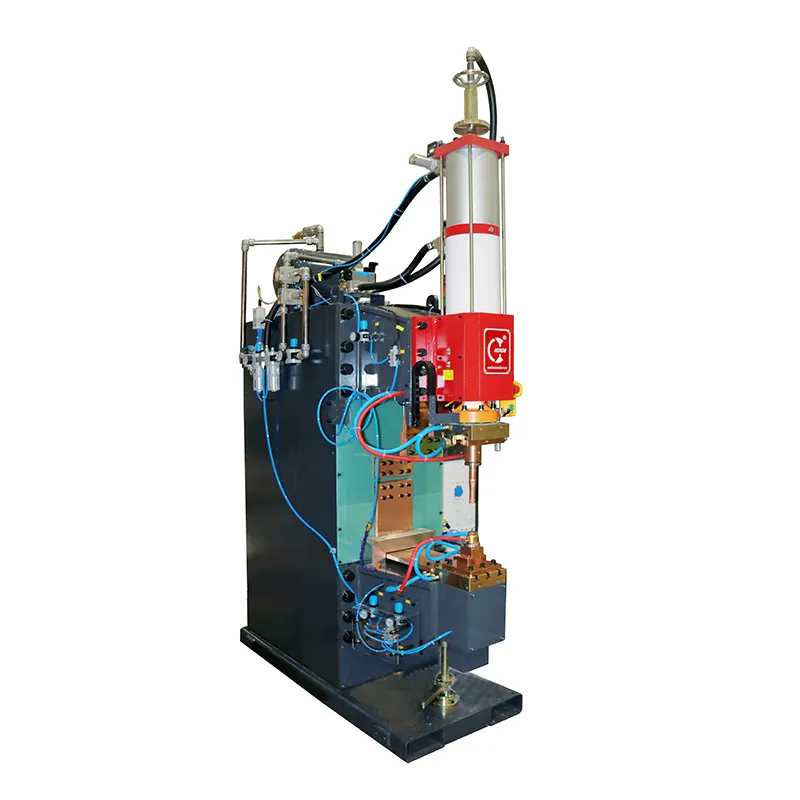
Factors affecting the welding performance of metal materials
The weldability of metal materials refers to the ability of metal materials to obtain excellent welding joints under conditions such as certain welding processes, including welding methods, welding materials, welding specifications and welding structural forms. A metal, if it can be used in more common and If a simple welding process obtains excellent welding joints, it is considered that this metal has good welding performance. The weldability of metal materials is generally divided into two aspects: process weldability and use weldability.
1.Material factors
Materials include base metal and welding materials. Under the same welding conditions, the main factors that determine the weldability of the base metal are its own physical properties and chemical composition.
In terms of physical properties: factors such as the melting point, thermal conductivity, linear expansion coefficient, density, heat capacity and other factors of the metal all have an impact on processes such as thermal cycle, melting, crystallization, phase change, etc., thereby affecting weldability. Stainless steel and other materials have low thermal conductivity. Materials with large temperature gradient, high residual stress and large deformation during welding.
In terms of chemical composition, the carbon element has the greatest influence, which means that the carbon content of the metal determines its weldability. As the carbon content in the steel increases, the hardening tendency increases, the plasticity decreases, and welding is easy to occur. Cracks. Therefore, the higher the carbon content, the worse the weldability. Low carbon steel and low alloy steel with a carbon content of less than 0.25% have excellent plasticity and impact toughness. The plasticity and impact toughness of the welded joint after welding are also very good. Welding There is no need for preheating and post-weld heat treatment, and the welding process is easy to control, so it has good weldability.
Welding materials directly participate in a series of chemical metallurgical reactions during the welding process, which determine the composition, structure, performance and formation of defects of the weld metal. If the welding materials are improperly selected and do not match the base metal, not only will it be impossible to obtain a joint that meets the usage requirements, but also It will introduce the occurrence of defects such as cracks and changes in structural properties. Therefore, the correct selection of welding materials is an important factor in ensuring high-quality welded joints.
2. Process factors
Process factors include welding method, welding process parameters, welding sequence, preheating, post-heating and post-weld heat treatment, etc. Welding method has a great influence on weldability, mainly in two aspects: heat source characteristics and protection conditions.
The heat sources of different welding methods are very different in terms of power, energy density, maximum heating temperature, etc. Metals welded under different heat sources will show different welding properties. For example, electroslag welding has high power but low energy density. , the maximum heating temperature is not high, the heating is slow during welding, and the high temperature residence time is long, resulting in coarse grains in the heat-affected zone and a significant reduction in impact toughness, which must be improved by normalizing treatment. In contrast, electron beam welding, laser welding, etc. This method has low power, but high energy density and rapid heating. The high temperature residence time is short, the heat affected zone is very narrow, and there is no danger of grain growth.
Adjusting the welding process parameters, taking other process measures such as preheating, postheating, multi-layer welding and controlling interlayer temperature, can adjust and control the welding heat cycle, thereby changing the weldability of the metal. For example, preheating before welding or after welding By taking measures such as heat treatment, it is entirely possible to obtain welded joints without crack defects and meeting performance requirements.
3. Structural factors
It mainly refers to the influence of welding structure and welding joint design form, such as structural shape, size, thickness, joint groove form, weld layout and cross-sectional shape, etc. on weldability. Its influence is mainly reflected in the heat transfer and force In terms of the state, different plate thicknesses, different joint forms or groove shapes have different heat transfer speed directions and heat transfer rates, which affect the crystallization direction and grain growth of the molten pool. The switch of the structure, the plate thickness and the welding seam The layout, etc., determines the stiffness and restraint of the joint, which affects the stress state of the joint. Poor crystalline morphology, severe stress concentration and excessive welding stress are the basic conditions for the formation of welding cracks. Reduce the stiffness of the joint during design. Reducing cross welds and reducing various factors causing stress concentration are important measures to improve weldability.
4. Conditions of use
It refers to the working temperature, load conditions and working medium during the service period of the welded structure. These working environment and operating conditions require the welded structure to have corresponding performance. For example, the welded structure working at low temperature must have brittle fracture resistance; working at high temperature The structure should have creep resistance; the structure working under alternating loads should have good fatigue resistance; the welded container working in acid, alkali or salt media should have high corrosion resistance, etc. In short, the better the use conditions Harsh, the higher the quality requirements for welded joints, the harder it is to ensure the weldability of the material
Contact Person: Christina Liu
Tel: 86 20 87813325 / 86 20 87819588 / 86 20 87815075
Fax: 86 20 87813346
Address: No.63 Xin Yi Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong China 510990